Who are market makers?
Market makers are participants in the foreign exchange market who “make” the Bid and Ask prices. By “making”, we mean that the participants are the ones who provide these very important prices. These participants are the big brokerage firms, investment banks, and even moneyed individual traders.
The foreign exchange (Forex) market is a high-speed place where the velocity of money exchange is mind numbing. Many activities are going on where some are players hedging while others are scalping and so on. This means that the market lifts and hits bids almost immediately. For this liquidity to remain elevated there has to be players ready to buy or sell currency whenever one places an order. For retail market participants like you, one of the most useful trading tips is to know what market makers are and how their actions affect the forex market.
How do these players make the market?
From the foregoing, market makers are important participants on whose actions the forex market continues to operate. But making the market also comes with some perks. When setting the Bid and Ask prices, the market makers profit off of the spread. How do the market makers operate? You may wonder.
Let us use an example of a hypothetical brokerage firm called M&M Brokers. M&M Brokers is a brokerage firm that has operated in the forex market for 25 years now. In this period, the firm has made a name offering forex products to its clients. In addition, the broker participates in principle trading.
On this day, M&M Brokers offers to buy €1 at $1.3629. At the same time, the brokerage firm is willing to sell €1 at $1.3630. If other market participants buy the EUR at the set price, then we say that they have “Lifted the Order” at $1.3630. On the other hand, M&M Brokers is willing to buy 1 EUR at $1.3629. The moment a market participant accepts the bid, then we say the market participants “Hit the Bid” at $1.3629.
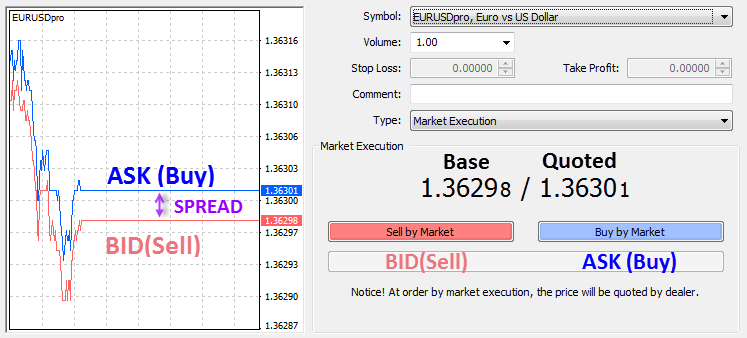
If you have followed closely, you will notice that the brokerage firm literally decided at what price the market can buy one Euro and at what price the market can sell one Euro. Herein is an explanation of how the market makers make money. The difference between the Bid price and the Ask price is what market participants call Spread. This spread is what amounts to the market maker’s profit.
In the case of M&M Brokers, the Bid Price (price at which the market maker will accept to buy1 EUR) was $1.3629. On the other hand, the Ask Price (price at which the market maker is willing to sell 1 EUR) was $1.3630. The difference, which is 0.0001, is the Spread. If M&M Brokers bought only 1 volume, then the profit is ($0.0001 x 1) = $0.0001. This might seem like a tiny sum but billions of exchanges take place in a single trading session. At the end of the day, market makers end up making millions in profits.
Where do market makers fit in the forex market structure?
The forex market is a hierarchy. At the very top are major banks that make up the interbank forex market. In this market, major banks transact with each other via platforms like Reuters Dealing 3000 and the Electronic Brokering Machine. At this level, there is little algorithmic trading because humans make most of the decisions and analysis.
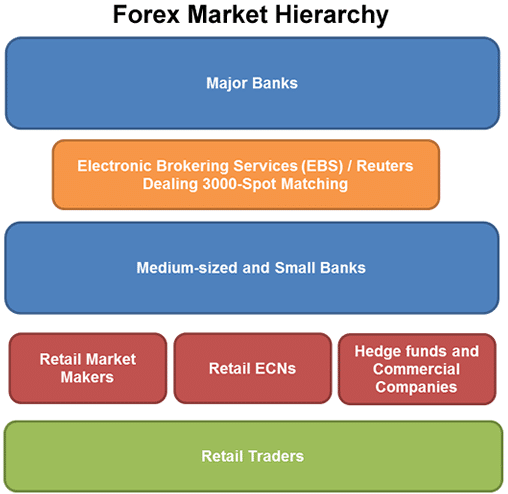
The players at this level are the real market makers. Below them are small and medium-sized banks, hedge funds, moneyed individuals, and large corporations. These players provide the link between retail traders like you and the rest of the hierarchy. Therefore, market makers can be anyone else but a retail market participant.
What is the significance of market makers?
As we have already seen, market makers set the Bid and Ask prices for the currency pairs in which they deal. How do they set these prices? Firstly, the market makers are in competition with each other. As such, the price that M&M Brokers offers might be better than that of its rivals in order to attract business. Secondly, the positions the market makers have taken in the market will determine their pricing.
Additionally, market makers commit to hold currency pairs temporarily from retail sellers. They may then sell these pairs to other retail sellers who want to buy. As a result, the market makers provide the much needed liquidity in the forex market. Thirdly, the market makers regulate the flow of money in the market. For example, if M&M Brokers realizes that there are too many sellers, the broker increases the spread by reducing the Bid price significantly. Subsequently, the resulting low selling price becomes unprofitable hence discouraging selling.
Another significance of market makers is that their actions are akin to a trading guide for retail market participants. One could use these actions as cues for entry and exit points for profitable trades. In addition to fulfilling orders for their clients, most of these market makers also trade on their behalf. Therefore, tracking their trading activities could lead you to major returns.