Forex/currency options is an instrument that allows FX traders to reap a couple of the benefits and thrills of transacting without going through the hassle of purchasing a currency pair.
Options contracts are similar to futures contracts. The difference is that when you use futures, you have to be committed to the agreement, unlike options, where you can choose whether to exercise the contract.
Why use forex options trading
Options traded in the forex market usually grant trades without the physical reception of assets. It also gives the merchants the power to set prices and expiry dates that meet risk cushions or gain plan demands when transacting forex options over-the-counter (OTC).
Additionally, merchants who use this financial instrument don’t have the responsibility to comply with the conditions of the agreement to buy or sell at expiry.
Furthermore, the premium paid is the only loss one can accrue when transacting forex options. This essentially means that their drawback risk is controlled, and their upward latent has no limit.
For the prevention of prospective losses in the FX market, every option agreement usually has an expiry date. Therefore, if the currency pair fails to hit the goal price, one can wait until the contract expires to keep the premium.
Unlike stocks, a forex trader can begin transacting with as little as a few dollars/pounds. The foreign currency market is open six days a week, 24 hours a day. As a result, the trader can get started in this business right away.
The foreign exchange market does not have a physical location because it deals with currency transactions that are not limited to a single country.
Forex options trading allows dealers to hedge their risks and reduce their losses.
Types of forex options trading
1. Call options
Call options provide dealers with a right, but not a responsibility, of purchase or of sale of any particular legal tender at a price and an expiry date agreed upon.
Additionally, buying of this financial instrument is done when there is a forecast of the currency prices movement upward, thus making profits off of the agreement.
The premium is the cost of purchasing the call option (it’s effectively the cost of purchasing the agreement that allows the purchase of the legal tender later). In this way, the call option premium is similar to a down payment on a home.
There is usually an agreement on the strike price between the purchaser and the seller. The purchaser is usually allowed an option to buy a certain currency amount before the expiry date.
2. Put options
If one believes the quoted currency will become stronger in comparison to the base currency before the close date, that will lead them to buy the forex put option.
Similarly, if a trader perceives that the price of the US dollar will climb against the value of the British pound, you can buy a GBPUSD put option. In this situation, the prospective gain would have no limit, while the losses would be controlled up to the cost of the options.
Additionally, if there is a feeling that the base currency will become stronger in comparison to the quoted currency, dealers usually tend to sell the forex put options.
Finally, limitless losses are incurred when the currency pair moves in the opposite direction, not favoring the merchant.
How forex options are traded
Traders of FX options can utilize the ‘Greeks’ to assess the prospects and rewards of the way the options are priced, just as they can for equities options.
For someone buying options, the risk is usually controlled by the cost of purchasing the option. In theory, the potential for making profits for someone trading in forex options has no limits.
On the contrary, the option seller risks are prospectively endless, making the profit to be restricted to the premium obtained.
If you want to use a currency trading system built around options selling, keep the two points below firmly in mind to get the odds even more on your side.
1. Sell greed buy fear
When a market is driven by greed and fear, option premiums rise, giving you the opportunity to trade and profit handsomely from your forex trading signals.
When markets deviate significantly from “fair value,” you sell. Here is an example of how to trade.
Check the percent bullish indicator (relative volatility index, RVI) as illustrated below for markets that are very bullish or bearish, and look for less than 15% bullish and more than 85% bearish to identify reversals.
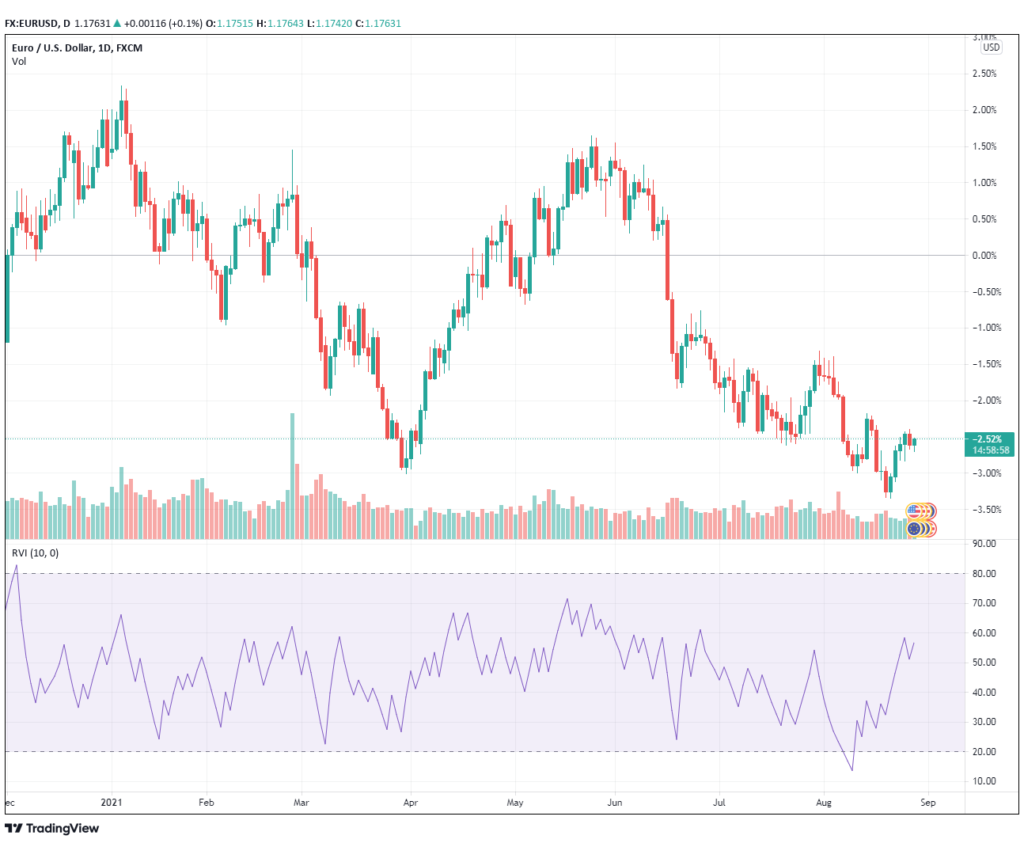
Then, using the commitment of traders’ data, seek for commercial purchasing of bear markets and selling of bull markets.
2. Time
When buying premium options, you want plenty of time on your side; when selling, the converse is true. Because time decay at the end of an option’s life kills it swiftly, take advantage of it by selling options with short expiration dates, allowing you to trade with 90% odds of success.
You may trade with a 90% chance of success and pile up large gains if you can acquire the right mindset, detect opportunities motivated by greed and fear, and dare to exploit them by selling currency options.
Forex options trading example
Assume a banker is optimistic about GBP and has a feeling that it will rise in price against USD. This would lead them to buy a forex option in anticipation of profit at the agreement expiration.
For Instance, the exchange rate is usually 100 times the quoted currency price. Therefore, if the strike price of the FX call option on the GBP is $215, the banker acquires it at this price. The spot rate of the GBP is comparable to $210 when the banker buys the contract.
Assume the spot price of the GBP is $218 on the close date of the agreement. Therefore, the currency option is in the money and is considered to have expired. The profit is $300, or 100 * ($218 – $215) less the premium paid for the currency option.
Conclusion
Trading forex options entails a multitude of ways that can be used to trade forex. A trader’s strategy is primarily determined by the type of option they select and the broker or platform via which it is made available.