In crypto, technical analysts often benefit from trading recognizable candlestick patterns such as the head and shoulders, cup and handle, and double and triple tops, just to mention a few. However, this may bring some level of success; it’s always helpful to incorporate supplemental indicators. Of these, one of the most widely used is the Relative Strength Index or RSI short. This indicator is used to help point out when an asset’s price has strayed away from its true value, indicating an incumbent market correction. This helps crypto traders better time their trade entries in this highly volatile market.
About the RSI
This is an indicator that shows the momentum and speed with which a crypto asset’s price moves. It is calculated by comparing the average upward price movement of a coin against the average downward price movement over time. It rates this on a scale of zero to one hundred. Extreme readings might indicate if a crypto asset is overbought or oversold.
How is the RSI obtained? The formula for calculating it is shown below.
RSI = 100 – (100/1 + RS)
The RS is the relative strength obtained by dividing all bullish closes over the last n periods by the total bearish closes over the same period.
By default, the number of periods used is 14. This means that for a daily chart, the RSI will be calculated for the last 14 days, while for a weekly chart, it covers the last 14 weeks. However, most charting platforms will allow you to tweak this number as you see fit.
How it works
The overbought signal
Uptrends are caused by more and more people buying into a crypto asset, which raises its demand and, consequently, its price. However, as the price gets higher, some buyers who had bought earlier start taking their profits, and as more of them liquidate their positions, supply starts outweighing the demand.
As an oscillator, the RSI tends to follow the direction of price movement. This means that during an uptrend, the indicator will trend upwards as well. When the rally starts losing momentum, the RSI will typically read above 70, indicating that the asset has been overbought. This usually signifies an incoming bearish reversal.
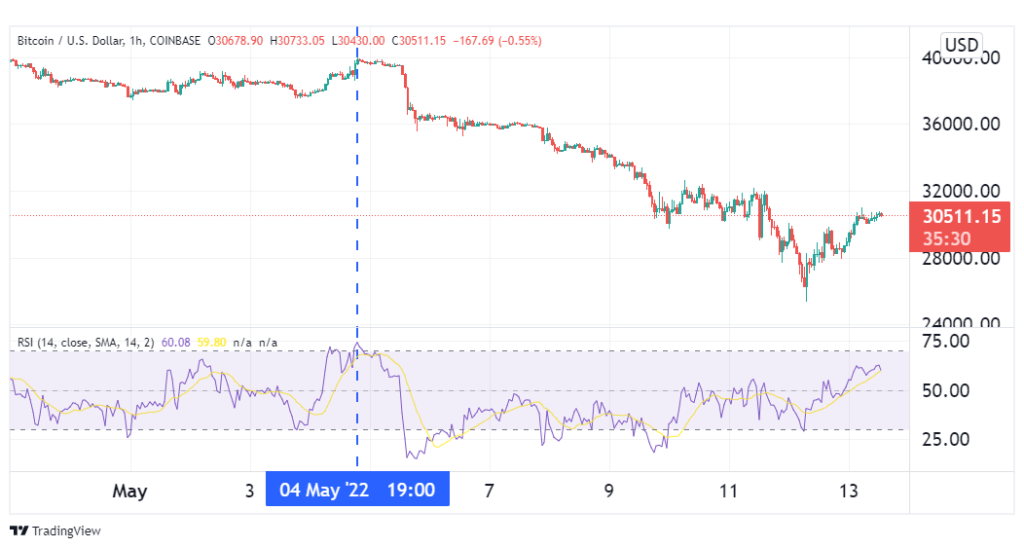
In the illustration above, we see the RSI marked BTC as overbought on 4th May. This was the signal for traders to go short on the asset. True to the signal, Bitcoin embarked on a downtrend shortly after.
The oversold signal
Similarly, during downtrends, the oscillator will typically plummet along with the price. When the RSI reads extreme values, usually below 30, it signifies that the trend’s momentum is waning. This is because the asset is oversold, and buying pressure is starting to overwhelm the bears. Usually, an oversold signal signifies an incoming bullish reversal. This is illustrated in the image below.
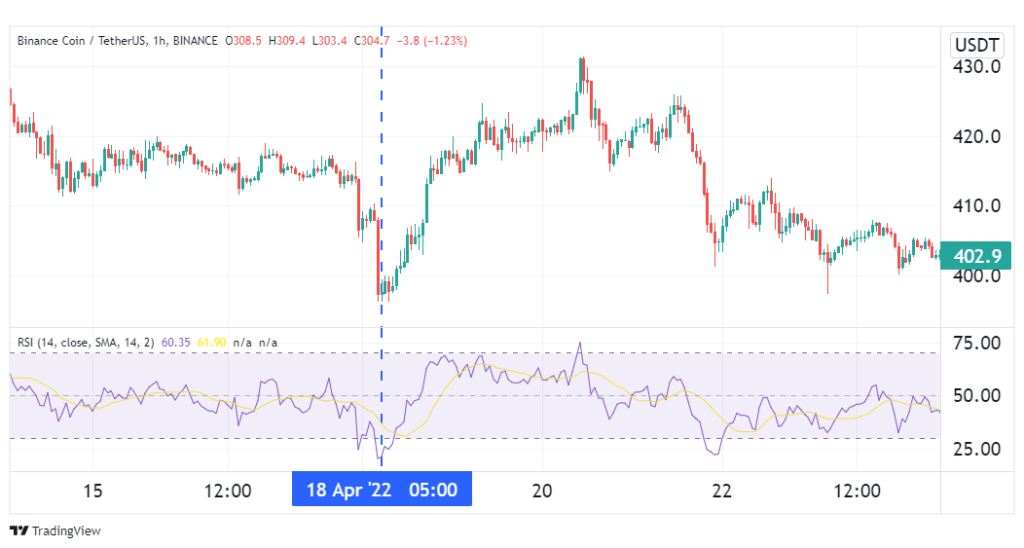
On 18th April, the RSI showed that Binance Coin was oversold, which is a bullish flag. True to this signal, the coin went on a sustained uptrend for the next few days.
Unfortunately, the RSI is not very accurate when used as a standalone indicator. It is prone to false signals, especially when the market experiences unexpected volatility. For that reason, it is always prudent to use it with another complementary indicator for the purpose of signal confirmation. Let’s look at some of the popular indicators used in conjunction with the RSI.
RSI + MACD strategy
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a tool used for determining the direction and velocity of a trend. A MACD line, a signal line, and a histogram make up the chart. A bullish flag is formed when the MACD line crosses above the signal while the histogram changes into positive territory. On the other hand, a bearish flag is formed when the MACD line passes below the signal, and the histogram becomes negative. These indications can be combined with RSI’s overbought and oversold signals, as seen below.
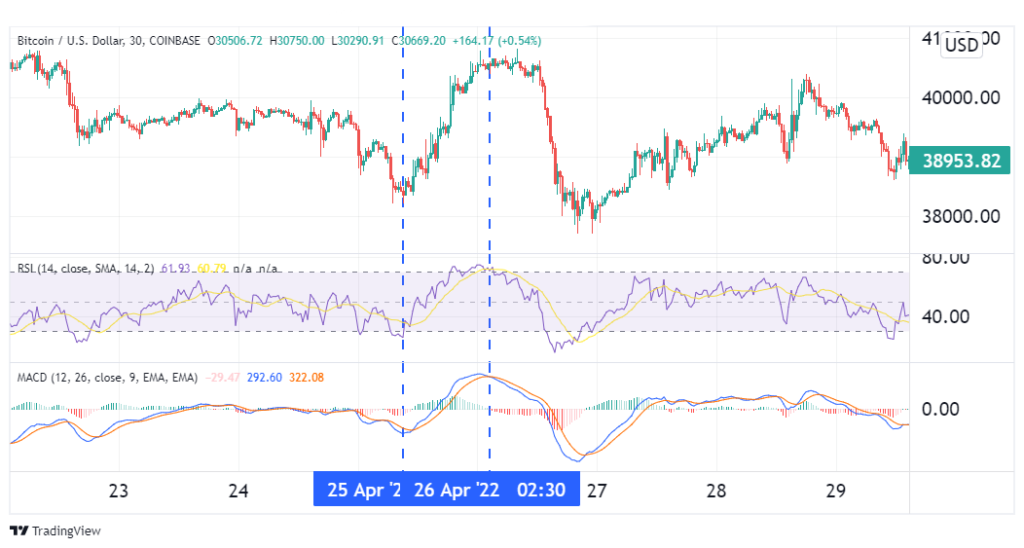
From the image above, RSI showed that Bitcoin was oversold on 25th April, a bullish flag. The signal was confirmed when shortly after, the blue MACD line crossed above the red signal line. This was the signal to buy the coin.
A day later, on the 26th, RSI gave the first bearish flag by going into overbought territory. Almost immediately, the MACD line crossed below the signal, confirming the bearish signal. This marked the exit of our long trade.
RSI + Bollinger Bands strategy
Bollinger Bands are an indicator used to depict whether prices are trending up or down on a relative basis. It utilizes a middle band which is a Simple Moving Average of the price, and two outer bands above and below it, separated from this middle band by a measure of standard deviations. When prices cross above the SMA to trend against the upper band, the market is bullish. If they cross below it to adhere to the lower band, the asset’s price is in a downtrend. This indicator can be used with the RSI, as seen below.
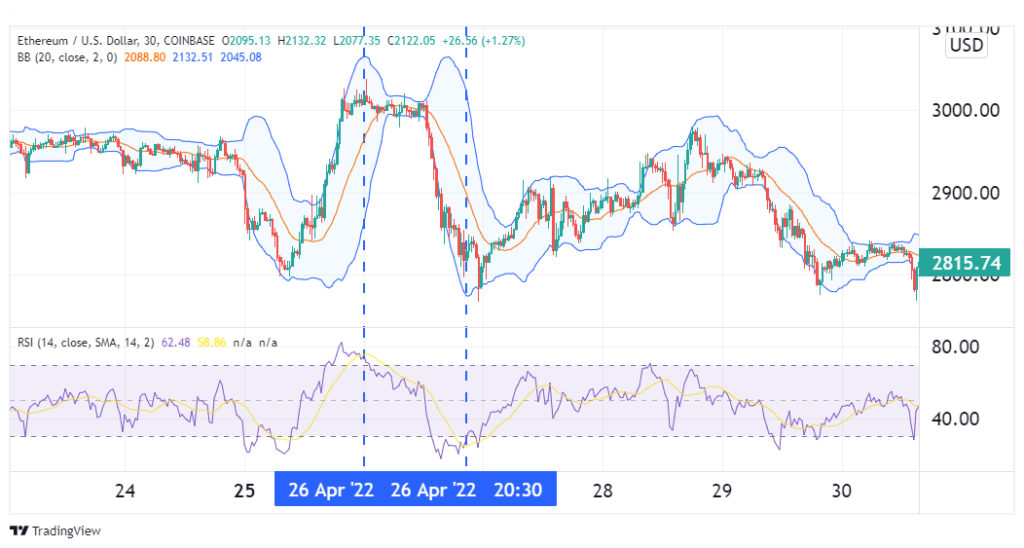
On 26th April, after a sustained rally, RSI indicated that Ethereum was overbought. This bearish signal was confirmed when shortly after, prices broke below the middle Bollinger Band to adhere to the lower. This marked the entry for a short trade. Later that day, RSI marked ETH as oversold. Shortly after, prices broke above the middle Bollinger Band, marking the exit for our short trade.
Conclusion
The RSI is a popular oscillator used in a variety of financial markets. In crypto, it can help identify whether an asset has been overbought or oversold, which can help traders better time their entries and exits. However, it is prone to false signals, which is why it is best to use it in combination with other indicators such as the MACD and Bollinger Bands.







