- New Zealand’s economy may shrink by 0.7% in 2021 owing to border closures in the new lockdown.
- The UK is expected to push through a trade deal with New Zealand that will lower tariffs on NZ’s main export products.
- Additional retracements of downward price movement indicate a strengthening pound against the NZD in 2021.
The British pound has dropped 12.22% against the New Zealand dollar since April 2020. The NZD remained stable as the country managed to sustain its elimination strategy of COVID-19 through outbreak detection, border biosecurity, and effective vaccination delivery. However, the pound sterling rose 2.09% against the NZD in the week leading to March 4, 2021. New Zealand’s Auckland was placed under a level-three lockdown after the emergence of a new British COVID-19 variant. Economic estimates show that New Zealand would lose about NZ $240 million, with Auckland bearing NZ $200 million of that amount. As part of its post-Brexit strategy, the UK is rushing to secure trade agreements with non-EU countries as part of its £217 billion trade worth realized as of 2019.
Low tariffs
The UK is planning to close Q1 2021 with a free-trade agreement with New Zealand. The deal will reduce tariffs on trade items such as wine, gin, and cars. The UK’s export of cars and coaches to New Zealand was worth £200m in 2020. This move is expected to increase UK export and promote fair play. It will be bullish for the GBP as compared to the NZD. However, Britain is still uncertain of its post-Brexit future as the EU postponed its decision to ratify the trade deal. In the end, the GBP may fall against the NZD as Britain seeks to protect its trade agreement with Northern Ireland.
Bilateral trade between the two countries as of 2019 was worth NZ$ 6 billion. The main trade exports to the UK at the time were meat, wine, machinery, and other agricultural products worth NZ$ 1.4 billion. Britain had the advantage with its commodity export totaling NZ$ 1.7 billion, leaving off a trade deficit of NZ$ 300 million on New Zealand’s side. COVID-19 has hampered New Zealand’s export services to the UK that has hampered travel and transport due to restrictions.
The main New Zealand exports that will be affected by the proposed trade deal agreement with the UK are shown below.
| Product | Tariff Percentage to be removed |
| Wine | £8.20-26.00 per hectoliter |
| Honey | 16% tariff |
| Seafood products | 20% |
| Onions, Kiwifruit, and apples | 8% |
The forbiddingly high tariffs on meat and dairy exports will also be affected.
New Zealand views the UK as a strategic trade partner, especially now that it is out of the EU’s restrictive environment. The EU is also in talks with Australia and New Zealand to reduce trade barriers as well as differing rules that act as trade barriers. Q4 2020 saw New Zealand bounce from a recession, pulling off a V-shaped recovery. Annual growth as of September 2020 was -2.2%, while the quarterly growth rose by 14.0% in the same period.
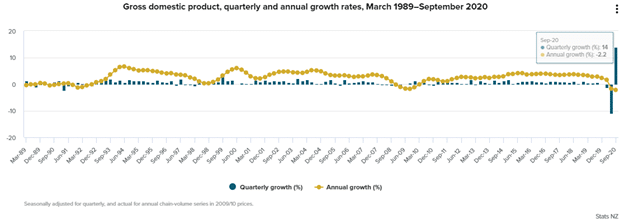
Border closures in 2021 may cause the economy to shrink further by 0.7% into the second quarter of 2021. However, the country is heavily reliant on the construction sector, especially as a source of employment. Property prices may rise by 17% before 2022 despite a slow monthly recovery.
Technical analysis
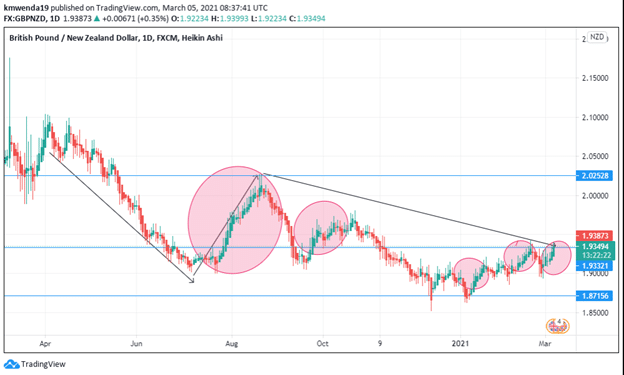
The GBP/NZD trading pair is struggling to maintain constant retracement levels as the British pound takes advantage of the lockdown situation in New Zealand. A stronger pound may force an upward price movement towards the 2.02528 marks where New Zealand forced a V-shaped recovery. We could still see a downtrend as the NZD emerges from the near recession fears and forces the trading pair towards the 1.87156 zones.







