The Canadian dollar, also known as the loonie, is a popular currency in the forex market. It is a currency major when it is paired with the US dollar and a minor when paired with other developed country currencies like the euro and sterling.
USDCAD vs EURCAD
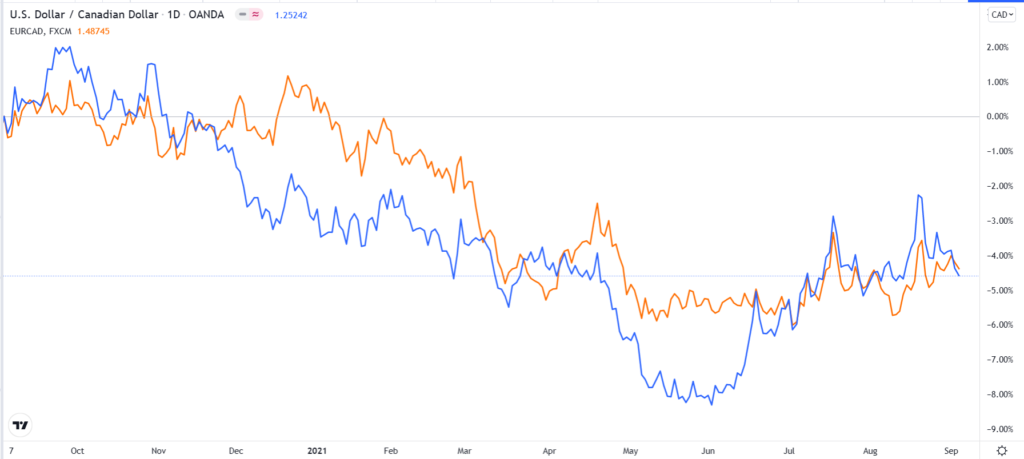
In this article, we will look at the Canadian economy and how to trade the Canadian dollar well.
The Canadian economy
Canada is a developed country that has a GDP of more than $1.7 trillion. This makes it the tenth biggest economy in terms of GDP in the world. It sits slightly above Brazil and Italy. The country has a population of almost 40 million people and a GDP per capita of about $47,000. This makes it the 24th wealthiest country in that measure.
Canada has a mixed economy. The most important components of the economy are manufacturing, mining, finance, and construction. The biggest constituent of the country’s GDP is household consumption.
Canada is a member of several important organizations. The most important one is the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which is now known as the United States, Mexico, and Canada Agreement (USMCA). The agreement allows the three countries to do a lot of business without tariff and non-tariff barriers.
The US is Canada’s most important trading partner. The two countries make the trade worth more than $720 billion every year. The US sells goods worth more than $360 billion, while Canada sells goods worth over $350 billion. Therefore, the happenings in the US tend to have a major impact on the Canadian dollar. The other leading Canada’s trade partners are the European Union, Japan, China, and Japan.
Canada exports many products. The leading ones are in the automobile industry since many American auto producers have operations in the country. Canada is also a leading oil and natural gas producer and exporter. It also sells a lot of precious metals like gold and silver,
Bank of Canada (BOC)
The Bank of Canada is often the key driver of the Canadian dollar. The bank is responsible for setting monetary policy such as interest rates, regulating commercial banks, and managing the money supply.
The bank’s monetary policy committee meets at least eight times per year to deliberate on the country’s economic situation. Like the Federal Reserve, the BOC has the mandate of ensuring that Canada has a low unemployment rate and that consumer prices are stable.
As a forex trader, you can always check out the dates of the Bank of Canada (BOC) meetings on the economic calendar. Ideally, when the economy is doing well, the BOC typically holds a hawkish policy. On the other hand, when things are not doing okay, the bank will typically cut interest rates.
The chart below shows the BOC interest rates since 1993. As you can see, the bank slashed interest rates during the dot com bubble, the Global Financial Crisis of 2008/9, and during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Bank of Canada interest rates since 1993
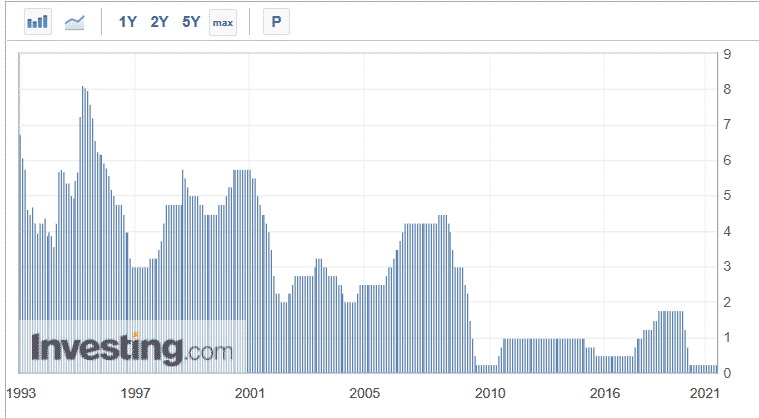
In extreme situations, such as during the Covid-19 pandemic, the bank tends to implement a quantitative easing (QE) program. QE is a period where a central bank boosts the money supply in the market by buying treasuries and other assets like mortgage-backed securities.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, the bank started buying C$6 billion per month and then gradually reduced the pace of asset purchases.
Therefore, as a Canadian dollar trader, it is important that you know when the bank has meetings and its recent decisions. Doing this will guide you to know whether to go long the loonie or short it.
Key Canadian economic data
In making its decisions, the BOC looks at key economic indicators. First, it looks at the state of the country’s labour market. Here, the regulator analyzes the total number of people who were added to the job market during the month, their wages, unemployment rate, and participation rate. In most cases, the central bank will typically be a bit hawkish when the job market is doing well. Statistics Canada usually publishes these numbers every month.
Second, the BOC looks at inflation. The two important gauges of inflation are the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI). The Canadian dollar will often hold steady against key currencies in a period of high inflation rates.
Other economic numbers it typically looks at are the performance of the manufacturing and services sector, retail sales, and industrial production.
Characteristics of the loonie
The Canadian dollar has several key unique characteristics. First, it is closely correlated with the price of crude oil since Canada is the fourth-biggest producer after the US, Saudi Arabia, and Russia. Therefore, the Canadian dollar tends to rise when oil prices rise and vice versa.
Second, the loonie has a close relationship with the United States economy because of the volume of trade between the two countries. When the American economy is doing well, it means that the Canadian economy will do good as well. Besides, as US consumer spending rises, demand for goods made in Canada will rise as well.
Third, traditionally, the Canadian dollar was seen as an important carry trade currency against the US dollar. That’s because Canada used to have higher interest rates than the US. Recently, however, the spread between the Canadian and the US has narrowed significantly, making it almost impossible to use the carry trade strategy. Still, you could employ the carry trade strategy using the Canadian dollar against the Swiss franc or Japanese yen.
Final thoughts
The Canadian dollar is a popular currency among day traders. Its most liquid counterpart is the US dollar, although other pairs like the EUR/CAD, GBP/CAD, and CAD/JPY are equally popular. In this article, we have looked at the unique characteristics of the loonie, the Bank of Canada, and some of the key economic numbers that move the currency.