Arbitrage is a popular trading technique, in which traders, as well as automated trading systems, try to exploit inefficiencies in asset pricing. The trading strategy has seen traders, as well as forex robots, make billions of dollars while also triggering some of the biggest financial collapses in the world.
Forex Arbitrage is simply a risk-free trading strategy whereby automated forex trading systems, as well as manual traders, try to make profits with no actual open currency exposure. The strategy entails responding fast to opportunities created in the market by pricing inefficiencies. Pricing inefficiencies don’t last long; therefore, it is the responsibility of traders to act quickly to make profits.
Unlike scalping trend trading or news trading strategies that seek to exploit price changes in a given market, arbitrage exploits discrepancies in the pricing of assets on two markets. Consider a security trading in two markets, i.e. the London Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange. If the asset is trading at different prices in the two markets, traders often buy in one of the markets, and they sell the same item in the other market.
Arbitrage Trading Strategies
Forex Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage is a common trading strategy whereby traders, as well as automated FX trading systems, use more than one trade to profit from price inefficiencies. The trading strategy is a precept of professional traders as well as Algorithmic FX trading systems that specialize in cross currency pairs.
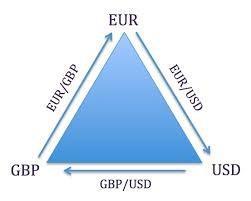
The arbitrage trading technique takes advantage of the fact that the exchange rate of cross-currency pair such as EUR/GBP is mathematically related to normal pairs such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD. In this case, three currency pairs are involved. Consider EUR/USD is going for 1.1500 at Bank A. EUR/GBP exchange rate in Bank B, on the other hand, is 1.200 while GBP/USD exchange rate at bank C is 1.2500.
In this case, a trader could go to Bank A and exchange $100,000 ($100,000 x1.1500) for EUR to get €115,000. The trader will then go to bank B and exchange the Euro to British Pound (115,000/1.2) to get £95,833.
The trader will then go to Bank C and convert the £95,833 back to dollars. In this 1.2500 x 95,833= $119,792.
A closer look, it is clear that the trader started with $100,000 but has ended up with $119,792 a net profit of $19, 792.
Once all the profit is locked in with the triangular arbitrage trading strategy, no further market risk exists.
Two Currency Arbitrage Trading Strategy
Two-currency arbitrage is the simplest arbitrage trading strategy that any trader can deploy without having to rely on an automated FX trading system. It is the most popular arbitrage trading strategy that involves trading the same currency, but in this case, in different brokers or markets all in the effort of exploiting their discrepancies in pricing.
Assume two banks:
Bank ABC is buying Euro at $1.2500 and selling them at $1.2700.
Bank XYZ buying Euro at $1.2800 and selling at $1.300.
In this case, a trader could buy Euro worth $100,000 from Bank A and consequently receive ($100,000 / 1.2500=€ 80,000). The trader will then go to Bank XYZ and convert the Euros to Dollars (80,000 x 1.28= $102,400). It is clear that the trader ended up netting a net profit of $2,400.
A trader would need to act as quickly as possible and carry out the two trades because as soon as more traders notice the discrepancy in prices, forces of supply and demand would cause the banks to adjust pricings.
Covered Interest Arbitrage Trading
Covered interest arbitrage is a trading strategy whereby traders try to exploit interest rate differences between two currencies. In this case, the use of a forward contract to control exposure to risk comes into play.
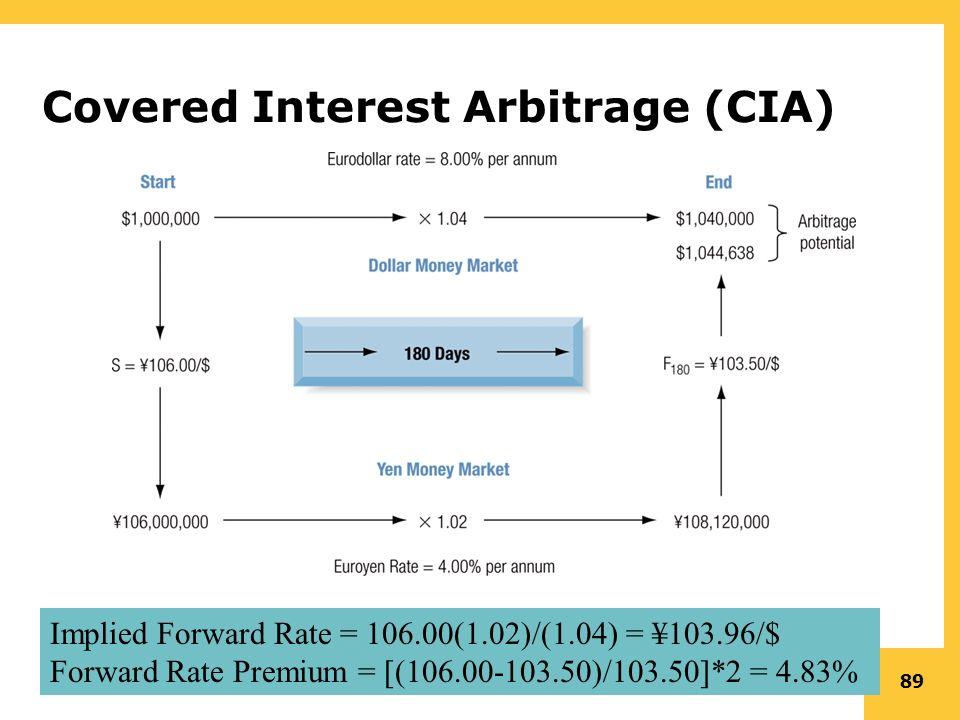
Consider a trader with $100,000 who identifies that the euro currency is trading at an interest rate of 4.8% compared to the dollar, which is at an interest rate of 3.4%. At an exchange rate of 1.2500, the trader could convert the dollars to euro ($100000/1.2500= €80,000).
To protect himself from exchange rate risk, the trader could take out a forward contract that locks in the $1.2500 exchange rate in the EUR/USD for a year. The trader will then invest the new €80,000 at a 4.8% interest rate to get a profit of $3,840, resulting in a total of $83,840.
Changing the $83,840 at the set exchange rate of 1.2500 will result in $104,800, which amounts to a net profit of $4,800 on the initial $100,000 capital.
Bottom Line
Arbitrage is an efficient trading strategy of exploiting market inefficiencies when it comes to pricing to generate profits. However, it is important to note that pricing inefficiencies don’t last long as markets often balance themselves out depending on forces of supply and demand in the market. For this reason, traders often use automated trading systems to capitalize before markets adjust themselves.