EURUSD represents two of the most actively traded currencies globally in the US dollar (USD) and euro (EUR). This pair is often known as the ‘euro’ or colloquially referred to as ‘fiber’ in some trading circles.
The nickname forming the latter term has a few origin stories. Many believe it’s because fiber optics are an upgraded version of ‘cable’ (the British pound) since the euro is a much newer currency.
Regardless, plenty of research suggests this market attracts the most trading volume daily for many years now, and it’s clear to see why.
For starters, the dollar and euro are the global reserve currencies, with the trillions worth of banknotes circulating the world every year. Therefore, if any forex transaction isn’t denoted in USD, it’s more than likely euro-based.
America is a global powerhouse on its own. Yet, when combined with the 19 member states of the European Union, this adds another layer to the economic dominance underlying the two currencies.
When viewing the exchange rate, EURUSD represents how many dollars it takes to purchase one euro. If we account for the pair’s current price, 1.12 dollars are equal to one euro.
So, in a nutshell, what moves the euro, and why? We’ll explore some of this pair’s fundamental drivers in more detail.
Characteristics of EURUSD
EURUSD is the #1 traded currency pair in foreign exchange. The massive economic interest induced by investors globally makes this pair structurally favorable for all trader types.
The euro has the lowest spread in the industry, yet another reason why it’s so attractive to trade. With most brokers during much of the trading day, traders don’t pay over a one-pip spread.
While EURUSD is a keenly-speculated major pair with massive liquidity, it’s technically not the most volatile market. Yet, the volatility isn’t necessarily poor, and price movements are hardly ever erratic.
Therefore, most traders consider EURUSD as reasonably predictable based on how it’s performed historically.
Technically, the euro is stronger than the dollar. However, the price action for this market is never a one-sided affair. We can see plenty of bull and bear markets for this pair over the years, as evident on the monthly chart below.
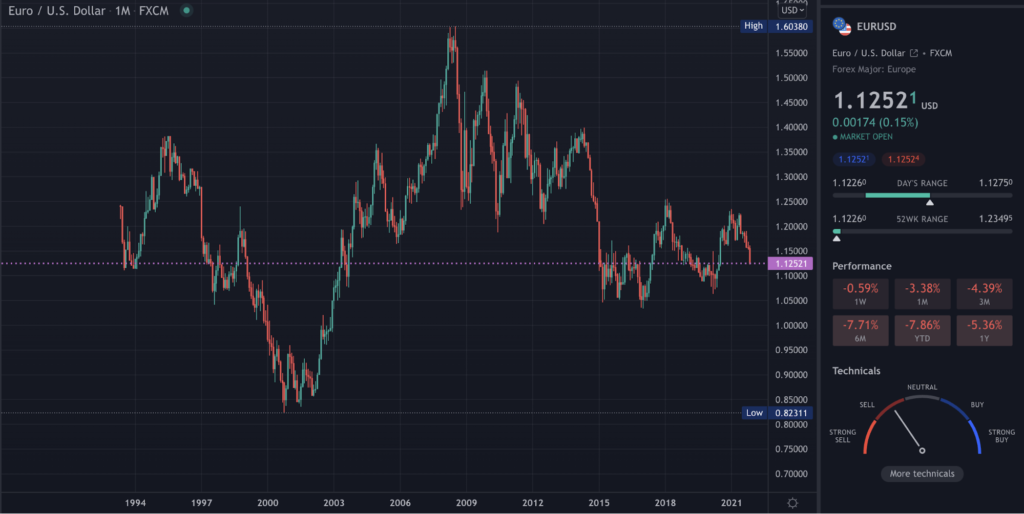
EURUSD uses a free-floating exchange rate mechanism, meaning supply and demand dictate this pair’s price. More specifically, particular fundamental factors are the underpinning drivers for this market. So, let’s explore a few of them below.
Interest rates
Monetary policies mainly determine the use of mainstream currencies, and interest rates are considered the primary indicator. The central banks governing the euro and US dollar are the European Central Bank (ECB) and Federal Reserve (or Fed), respectively.
Like any central bank, the main job of these groups is stimulating the economy and ensuring there isn’t too much inflation. The rule of thumb is that a central bank typically cuts interest rates to boost the economy and hikes the rates to decrease inflation.
When the former happens, it makes the currency less valuable. A rate cut is accompanied by less foreign investment; citizens have no motivation to save their money, and so on. Conversely, a higher interest rate makes the currency more valuable; more significant foreign investment and saving occur due to the attractive rates, etc.
The ECB’s current interest rate is 0% (which it has held for several years), while the Fed has a 0.25% rate. In the long term, the euro has been weaker against the US dollar partly because of this rate.
By applying an exponential 200-day Moving Average on the chart, it suggests a downtrend.
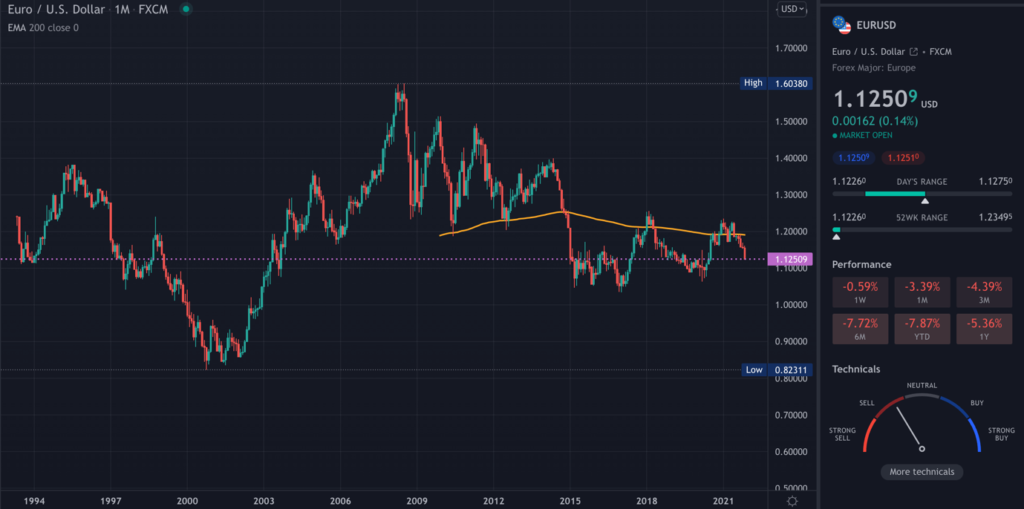
If the ECB were, at any stage, to decide on a rate hike, it would likely push the EURUSD up; should the rate stay the same after a new report, it’s probable the opposite will happen.
Let’s not forget traders will also watch the new reports from the Fed and compare its interest rate with that of the ECB. Overall, interest rates often dictate the long-term outlook of any currency pair, and in the case of EURUSD, they are one of the central drivers moving the pair.
Inflation
Inflation is another factor affecting interest rates and the overall supply and demand of a currency. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is the main index of measuring this phenomenon.
This indicator can influence short-term price movements as the data is released more frequently (monthly) than interest rates and can change regularly, unlike the latter, which has remained constant for years.
It’s worth noting that new CPI data for the euro and US dollar aren’t released simultaneously. Yet, analysts will compare the two figures and see which country has the upper hand. The release day is one of the most critical periods to analyze.
Generally, if the euro’s CPI is higher than the previous month, the EURUSD exchange rate will probably surge, and vice versa. Conversely, if the dollar’s CPI comes out lower than previously, EURUSD should increase in value, and vice versa.
US dollar index
The dollar index (DXY/USDX) is an index measuring the value of USD against a basket of predominantly major currencies, namely the euro, Japanese yen (JPY), British pound (GBP), Swiss franc (CHF), Canadian dollar (CAD), and Swedish krona (SEK).
Generally, the DXY often has an inverse relationship to USD-based pairs. EURUSD makes up the largest component of the index, accounting for close to 60%. Therefore, if DXY is moving up, the euro is probably moving down; the opposite is true.
The drivers of the index are some of the fundamental indicators we’ve outlined, like the interest rates and inflation figures for the US dollar. Traders should undoubtedly observe the DXY as it’s a more practical way of seeing the ‘blow by blow’ action between it and the major pairs overall.
Final word
It’s easy to understand why the euro forms part of the portfolio of nearly all traders. Plenty of regularly-updated technical and fundamental data exists for analysts to observe and exploit.
Whether you scalp the markets or hold your positions for long periods, EURUSD is action-filled. But like any forex pair, ‘out of the ordinary’ things can and have happened before.
Therefore, one should appreciate how dynamically any forex pair can behave and trade in a risk-centric manner.